Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
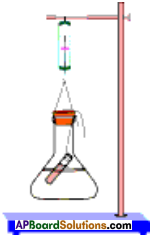
Draw the diagram to show the experimental setup for the law of conservation of mass. (AS 5)
(OR)
Draw the experimental arrangement used in verifying law of conservation of mass. Write the law of conservation of mass.
Answer:
Question 2.
Explain the process and precautions in verifying law of conservation of mass. (AS 5)
(OR)
Explain the procedure to prove in a chemical reaction the mass neither destroyed.


Answer:
Aim :
To verify law of conservation of mass.
Material required :
Sodium sulphate,Barium chloride, distilled water, conical flask, spring balance, small test tube, rubber cork, thread, retort stand.
Procedure:
- Prepare a solution of sodium sulphate by dissolving approximately 2 gm of sodium sulphate in 100 ml distilled water in a 250 ml conical flask.
- Prepare a Barium chloride solution by dissolving approximately 2 gm of potassium iodide in 100 ml water in another conical flask.
- Take 100 ml solution of sodium sulphate in 250 ml conical flask.
- Also take 4 ml solution of Barium chloride in test tube.
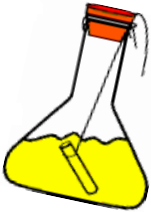
- Hang the test tube in the flask carefully without mixing the solutions. Put a cork on the flask.
- Weigh the flask with its contents carefully by spring balance.
- Now tilt and swirl the flask, so that the two solutions mix.
- Weigh the flask again by the spring balance.
Observations:
- Weight of flask and contents before mixing = m1g
- Weight of flask and contents after mixing = m2g
Conclusion :
- We have observed that the two weights i.e., mj and m2 are equal.
- This proves the law of conservation of mass.
Precautions:
- Care should be taken while handling chemicals.
- Glass apparatus may slip and break down. Hence make sure that they should not slip from your hands.
- Contents of the conical, ffhsk should not mix before weighing first time.
- Tie a thick thread to the conical flask, so that it will not slip while weighing.
Question 3.
15.9g of copper sulphate and 10.6g of sodium carbonate react together to give 14.2g of sodium sulphate and 12.3 g of copper carbonate. Which law of chemical combination is obeyed? How? (AS 1, AS 2)
Answer:
Reactants:
Mass of copper sulphate = 15.9 g ; Mass of sodium carbonate = 10.6 g
Total mass of reactants = 15.9 + 10.6 = 26.5 g
Products:
Mass of sodium sulphate = 14.2 g ; Mass of copper carbonate = 12.3 g
Total mass of products = 14.2 + 12.3 = 26.5 g
∴ Total mass of reactants is equal to total mass of products. This is the “Law of conservation of Mass”.
Question 4.
Carbon dioxide is added to 112 g of calcium oxide. The product formed is 200 g of calcium carbonate. Calculate the mass of carbon dioxide used. Which law of chemical combination will govern your answer? (AS 1, AS 2)
Answer:
- Let x g of carbon dioxide is added to 112 g of calcium oxide.
- The product is 200 g of calcium carbonate.
- According to law of conservation of mass, ,
Total mass of reactants = Total mass of products
x+ 112 = 200 g
x = 88 g
∴ 88 g of carbon dioxide is used.
Question 5.
0.24 g sample of compound of oxygen and boron was found by analysis to contain 0.144 g of oxygen and 0.096 g of boron. Calculate the percentage composition of the compound by weight. (AS 1)
Mass of compound of oxygen and boron = 0.24 g
On analysis,
Mass of oxygen in the compound = 1.44 g
Mass of boron in the compound = 0.096 g
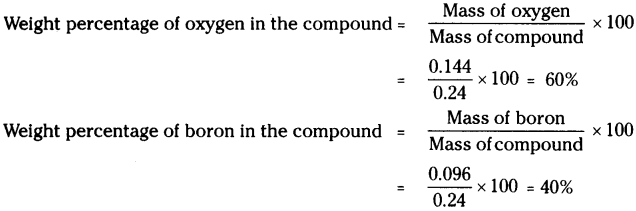
Question 6.
In a class, a teacher asked students to write the molecular formula of oxygen. Shamita wrote the formula as 02 and Priyanka as O. Which one is correct? State the reason. (AS 1, AS 2)
Answer:
Shamitha’s answer is correct.
Reason :
- Oxygen is diatomic.
- Two atoms of oxygen combine to form oxygen molecule.
- Hence the formula of oxygen molecule will be ‘O2‘.
Question 7.
Imagine what would happen if we do not have standard symbols for elements. (AS 2)
(OR)
Is it necessary to use symbols for elements? Write your opinion.
Answer:
- Chemistry involves a lot of reactions.
- If we do not have symbols, we have to write their names to represent the reactions.
- This is very tedious work.
- To avoid this, we need standard symbols to elements, which are universally accepted.
- In advanced studies, balancing of equations, atoms present in a compound, etc. will not be understood without symbols.
- Simply chemistry will not be developed unless symbols, formulae, etc. are not known.
Question 8.
Mohith said “H2differs from 2H.” Justify. (AS 1)
Answer:
H2is the hydrogen molecule in which two hydrogen atoms are combined to form one hydrogen molecule.
2H is the hydrogen atom. Here 2 hydrogen atoms are ready to participate in chemical reaction.
Question 9.
Lakshmi gives a statement “CO and Co both represent element”. Is it correct? State reason. (AS 1, AS 2)
Answer:
Lakshmi’s statement is incorrect.
Reason :
- CO stands for carbon monoxide, a compound, which consists carbon and oxygen atoms.
- This can be identified with the help of both C and O are capital (upper case) letters.
- Co stands for cobalt, an element.
- This can be identified with the help of ‘C’ is capital (upper case) letter and ‘o’ small (lower case) letter.
Question 10.
The formula of water molecule is H2O. What information do you get from this formula? (AS 1)
Answer:
- Water is a combination of hydrogen and oxygen.
- Two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom combine to form one water molecule.
- Molecular weight of water molecule is 18. [Hydrogen 1, Oxygen 16. H2O ⇒ 2 × 1 + 16=18]
- 18 g of water molecule contains 6.022 × 1023particles in it.
- Valency of hydrogen is 1 and oxygen is 2.
Question 11.
How would you write 2 molecules of Oxygen and 5 molecules of Nitrogen? (AS 1)
Answer:
2 molecules of oxygen → 2O2
Reason :
- Oxygen is diatomic element.
- Two oxygen atoms combine to form one oxygen molecule.
- The formula of oxygen molecule is O2.
5 molecules of nitrogen → 5N2
Reason :
- Nitrogen is also diatomic element.
- Two nitrogen atoms combine to form one nitrogen molecule.
- Molecular formula of nitrogen is N2.
Question 12.
The formula of a metal oxide is MO. Then write the formula of its chloride. (AS 1)
Answer:
- The valency of oxide is 2 i.e., O-2.
- The formula of a metal oxide is given as MO.
- Hence the valency of the given metal must be 2 i.e., M+2.
- Valency of chloride is 1 i.e., C-.
- Therefore according to criss-cross method, the formula of given metal chloride will be MCl2.
Question 13.
Formula of calcium hydroxide is Ca(OH)2and zinc phosphate is Zn3(PO4)2. Then write the formula to calcium phosphate. (AS 1)
(OR)
Formula of calcium hydroxide is Ca(OH)2and zinc phosphate is Zn3(PO4)2. Then write the valencies of calcium and phosphate and then write the formula of calcium phosphate.
Answer:
- Formula of calcium hydroxide is Ca(OH)2.
- From criss-cross method we know that the valency of calcium is 2 i.e., Ca+2and hydroxide is 1 i.e., OH–.
- Formula of zinc phosphate is Zn3(PO4)2.
- Valency of Zn is 2 i.e., Zn+2,and valency of phosphate is 3 i.e., PO4-3.
- Now the formula of calcium phosphate according to criss-cross method is Ca3(PO4)2.
Question 14.
Find out the chemical names and formulae for the following common household substances. (AS 1)
a) Common salt
b) Baking soda
c) Washing soda
d) Vinegar
Answer:
| Common household substance |
Chemical name |
Formula |
| a) Common salt |
Sodium chloride |
NaCl |
| b) Baking soda |
Sodium bicarbonate |
NaHCO3 |
| c) Washing soda |
Sodium carbonate |
Na2CO3 |
| d) Vinegar |
Impure dilute acetic acid |
CH3COOH |
Question 15.
Calculate the mass of the following. (AS 1)
a) 0.5 mole of N2gas
b) 0.5 mole of N atoms
c) 3.011 × 1023number of N atoms
d) 6.022 × 1023number of N2molecules
Answer:
a) 0.5 mole of N2gas :
Mass of one mole of N2gas = 28 g. (∵ Molecular wt. of N2= 28)
Mass of 0.5 mole of N2gas = 28 × 0.5 = 14 g
b) 0.5 mole of N atoms :
Mass of one mole of N atoms = 14 g (∵ Atomic wt. of N = 14)
Mass of 0.5 mole of N atoms = 14 × 0.5 = 7 g
c) 3.011 × 1023number of N atoms :
Mass of 6.022 × 1023number of N atoms = 14 g
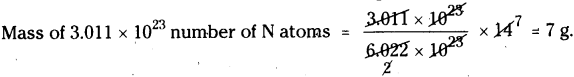
d) 6.022 × 1023number of N2molecules :
Mass of 6.022 × 1023number of N2molecules = 28 g
Question 16.
Calculate the number of particles in each of the following. (AS 1)
a) 46 g of Na
b) 8 g of O2
c) 0.1 mole of hydrogen
Answer:
a) 46 g of Na :
Atomic weight of Na = 23
Number of particles in 23 g of Na atom = 6.022 × 1023
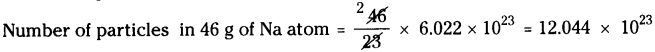
b) 8 g of O2:
Molecular weight of O2is 32.
Number of particles in 32 g of O2 molecule = 6.022 × 1023
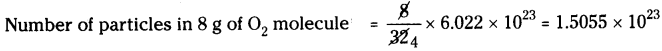
c) 0.1 mole of hydrogen :
Atomic weight of hydrogen is 1.
Number of particles in 1 mole of hydrogen = 6.022 × 1023
Number of particles in 0.1 mole of hydrogen=0.1/1× 6.022 × 1023= 6.022 × 1022
Question 17.
Convert into moles. (AS 1)
a) 12 g of O2gas
b) 20 g of water
c) 22 g of carbon dioxide
Answer:
a) 12 g of O2gas :
Molecular weight of O2is 32.
∴ Number of moles of 32 g of O2gas = 1
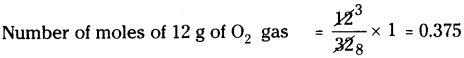
b) 20 g of water :
Molecular weight of water (H2O) is 18.
Number of moles of 18 g of water = 1
Number of moles of 20 g of water = 20/18 x 1 =1.11
c) 22 g of carbon dioxide :
Molecular weight of carbon dioxide (CO2) is 44.
∴ Number of moles of 44 g of CO2 = 1
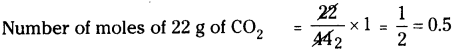
Question 18.
Write the valencies of Fe in FeCl2and FeCl3. (AS 1)
Answer:
- In FeCl2, the valency of Fe is 2.
- In FeCl3, the valency of Fe is 3.
Question 19.
Calculate the molar mass of sulphuric acid (H2SO4) and glucose (C6H12O6). (AS 1)
Answer:
a) Formula of sulphuric acid is H2SO4.
Molecular mass of H2SO4= 2 × 1 + 1 × 32 + 4 × 16 = 2 + 32 + 64 = 98 u
∴ Molar mass of H2SO4= 98 g
b) Formula of glucose is C6H12O6.
Molecular mass of C6H12O6= (6 × 12) + (12 × 1) + (6 × 16) = 72 + 12 + 96 = 180 u
∴ Molar mass of C6H12O6= 180 g.
Question 20.
Which has more number of atoms - 100 g of sodium or 100 g of iron? Justify your answer. (Atomic mass of sodium = 23 u, atomic mass of iron = 56 u) (AS 1)
Answer:
100g of sodium has more number of atoms than 100g of iron.
Justification :
1) Atomic mass of sodium = 23 u
23 g of sodium contains 6.022 × 1023atoms.
100 g of sodium contains =100/23× 6.022 × 1023= 26.1826 × 1023atoms of sodium.
2) Atomic mass of iron = 56 u
∴ 56 g of iron contains 6.022 × 1023atoms.
100 g of iron contains =100/56× 6.022 × 1023= 10.7535 × 1023atoms of iron.
Question 21.
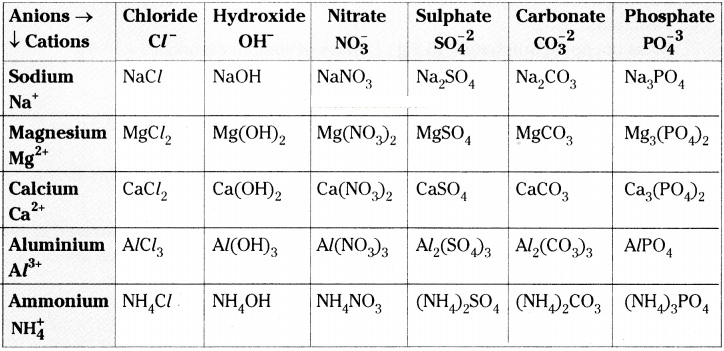
Complete the following table. (AS 1)
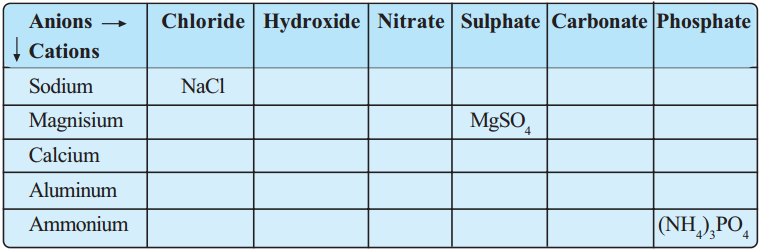
Answer:
Question 22.
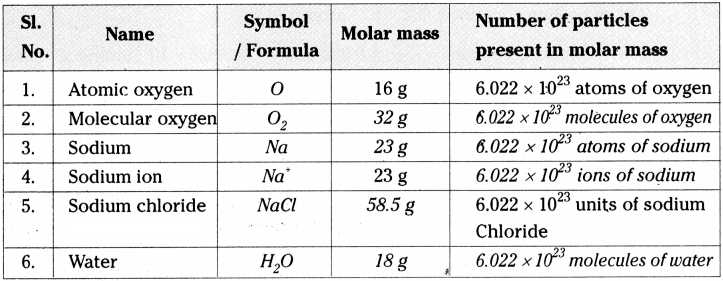
Fill the following table. (AS 1)
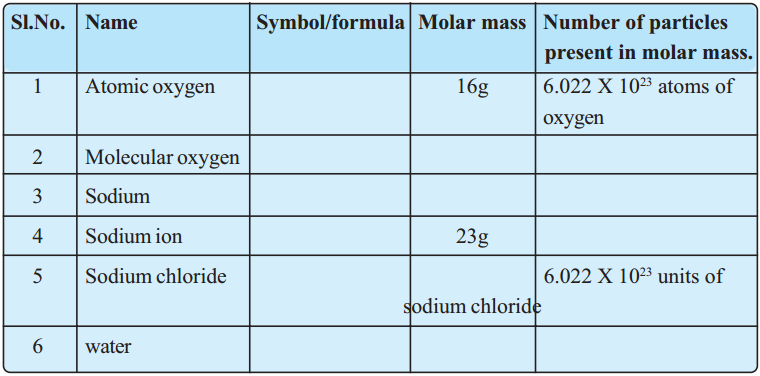
Answer:
Question 23.
Make placards with symbols and valencies of the atoms of the elements separately. Each student should hold two placards, one with the symbol in the right hand and the other with the valency in the left hand. Keeping the symbols in place, students should criss-cross their valencies to form the formula of a compound.
Answer:
Student’s activity.
Question 24.
Take empty blister packs of medicines. Cut them into pieces having
